

Home | Testing Services | Technical Information | Consulting | Customer Services | Careers | Contact Us
![]()
►TOYS
►REGULATIONS OF DIFFERENT COUNTRIES

R&TTE Directive – 1995/5/EC – EU Directive on radio equipment and telecommunications terminal equipment (R&TTE) and
the mutual recognition of their conformity
Introduction to the R&TTE Directive
The Radio and
Telecommunications Terminal Equipment (R&TTE) Directive has shifted the
burden of approving telecommunications and radio products for the European
market. Rather than requiring a long and costly approval process involving
certifying authorities, compliance is presumed when a manufacturer issues a
declaration of conformity (DoC).
The directive,
enacted by the European Union (EU) in April 2000, removed significant barriers
that prevented wireless communications products from freely circulating within
the EU. In addition to the normal cell and wireless phones, these systems
include wireless LANs, alarm systems, remote-entry systems, meter readers,
PDAs, video-game controllers, and keyboards. The opportunity represented by the
EU market makes it imperative for manufacturers to understand the R&TTE
Directive and how it applies to their products.
Scope of the Directive
The
sector of Radio-communications and
Telecommunications Terminal Equipment Industries encompasses all products
using the radio frequency spectrum (e.g. car door openers, mobile
communications equipment like cellular telephones, CB radio, broadcast
transmitters, etc.) and all equipment attached to public telecommunications
networks (e.g. ADSL modems, telephones, telephone switches). The competitive
situation of this industry is relatively good: the R&TTE is one of the few
high-tech sectors in which the EU industry has a globally leading position in
certain sub-sectors, being particularly competitive in the areas of cellular
communications and switching.
Routes to demonstrate compliance
The goal for a
manufacturer is to obtain the CE Marking by demonstrating compliance with the
R&TTE Directive. Several routes are available to reach that goal:
- Standards: the simplest path, described
in Annex III.
- Technical Construction File (TCF): used
for more complex cases and nonharmonized standards; requires a notified
body (NB), described in Annex IV.
- Full Quality Assurance: a manufacturer
declares compliance based on having an accredited quality system,
described in Annex V.
The standards and the
TCF routes are akin to the EMC Directive process and discussed here since most
products will fall within one route or the other. However, before choosing a
route for compliance, the manufacturer first must understand the essential
requirements of the directive:
- Frequency Spectrum: effective use to
avoid harmful interference.
- Electrical Safety and Health: as in Low
Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC.
- Electromagnetic Compatibility: as in
the EMC Directive 89/336/EEC
Standards Route
As a practical guide, this
section uses typical products to illustrate the routes to compliance. The
requirements addressed are in addition to those covered under internal
production control discussed previously. For compliance with the standards
route, a product manufacturer must have applied the appropriate harmonized
standard. To fully understand how to use the standards route, a definition of harmonized
standard is required. A standard is deemed to be harmonized once it has
been published in the OJEC. A list of standards was recently published
on
Complying with a harmonized standard does not ensure that a product meets the essential requirements of the directive, but rather gives the manufacturer a "presumption of conformity" with the essential requirements.
The
The TCF route to
compliance is slightly more involved because it requires the submission of a
complete technical package to an NB for review. This option typically is used
when harmonized standards do not exist such as in marketing new technologies or
when harmonized standards have been only partially applied.
It should be noted
that the TCF route may be chosen even if harmonized standards exist for a
product. Some manufacturers gain a level of confidence by submitting TCFs to
NBs for review—a third-party independent assessment.
An NB’s role includes
identifying test suites, reviewing the TCF, and issuing an opinion to the
manufacturer. By mandate, the opinion of an NB to the manufacturer must be
given within four weeks of receipt of the TCF.
At the end of four
weeks or upon the receipt of the opinion from the NB, the manufacturer or
authorized representative within the EU can label the product and place it on
the market. The label will have the CE Marking and the NB’s number. If the
device operates on a nonharmonized frequency band, then the ECI alert symbol
also must be placed on the label.
In the event that an
unfavorable opinion is received from an NB, it is the manufacturer’s
responsibility to notify all other NBs of the opinion. Even if an NB does not
issue a favorable opinion, the manufacturer still may decide to sell the
product that operates on a harmonized frequency band in the EU.
The NB’s opinion is
just that—an opinion. National authorities, however, may decide to have the
product withdrawn from the market if they reasonably expect that the product
could cause interference.
Quality-Assurance Route
The last route to
compliance, full quality assurance, is more complex and not as popular as the
other routes. This approach requires that the manufacturer have an accredited
quality system. This tacitly demonstrates that the manufacturer has the
necessary procedures and systems in place to ensure compliance with the
R&TTE Directive. Currently, only a few NBs are approved to check, approve,
and monitor quality-assurance systems.
The following points
summarize the requirements that a manufacturer must fulfill to achieve
compliance via the full quality-assurance route, as detailed in Annex V:
- Operate an approved quality system
covering design, manufacture, and final product inspection and test.
- Allow an NB inspection to ensure that
the quality system is sufficient and products will meet the essential
requirements of the directive.
- Permit regular audits by an NB for
continued compliance.
- Make all quality documentation,
technical locations, and documents available to the NB for inspection.
- Allow unscheduled NB audit visits.
- Produce and retain technical documents
referred to in section 3.2 of the directive and allow continued assessment
of these documents by an NB.
- Apply the relevant markings to products
placed on the market.
Quality system
approvals require that each NB make available relevant information concerning
the approval, including references to products issued and withdrawn, to all
other NBs. Once compliance is achieved, manufacturers can produce a DoC and
place a product on the market only if the equipment operates on a harmonized
frequency band.
If the device
operates on a nonharmonized frequency band, the manufacturer must wait until
the notification process has been completed. The equipment must be labeled with
the NB number, CE Marking, and ECI alert symbol if using a nonharmonized
frequency band.
Although the full
quality-assurance route is available, few manufacturers probably will use it.
In his article on the R&TTE Directive, Martin Green, director of Technology
International, commented, “There is no reason why manufacturers should use this
route, unless they have already established a similar route under the old
legislation….it would seem a somewhat complex and unnecessary method to achieve
certification.”1
Table summarizing the routes to compliance along with the requirements
for using an NB and the marking of the product
|
Route to Compliance |
Frequency-Band
Allocation |
Notified Body
Consulted |
Marking/Labeling |
|
Standards |
Harmonized |
No |
CE Marking |
|
Yes (optional) |
CE Marking |
||
|
NB Number |
|||
|
Nonharmonized |
No |
CE Marking |
|
|
ECI (Alert Symbol) |
|||
|
Yes (optional) |
CE Marking |
||
|
NB Number |
|||
|
ECI (Alert Symbol) |
|||
|
Technical Construction File |
Harmonized |
Yes |
CE Marking |
|
NB Number |
|||
|
Nonharmonized |
Yes |
CE Marking |
|
|
NB Number |
|||
|
ECI (Alert Symbol) |
|||
|
Full Quality Assurance |
Harmonized |
Yes |
CE Marking |
|
NB Number |
|||
|
Nonharmonized |
Yes |
CE Marking |
|
|
NB Number |
|||
|
ECI (Alert Symbol) |
Labeling
The Table above details the
labeling information required for the R&TTE Directive's routes to
compliance. Affixing the CE mark to the product indicates that the equipment
complies with all relevant CE marking directives, not necessarily just the
R&TTE Directive (see Figure 1).

Figure
1: CE Mark
The alert mark, as shown in
Figure 2, affixed to the product indicates that because the product does not
operate on a harmonized frequency band, it has restricted geographical areas of
use across the EU. The alert mark applies to so-called Class 2 equipment (as
opposed to Class 1 equipment that operates on a harmonized frequency band). The
following Tables provide the most recent lists of equipment specified in Class
1 and Class 2 categories. These lists are subject to change. An example of
product labeling is depicted in Figure 3. The XXXX represents the number of the
notified body. Other labeling requirements encompass the need for information
to be supplied to end-users and to be provided on product packaging.

Figure 2: Equipment class identifier (alert mark)
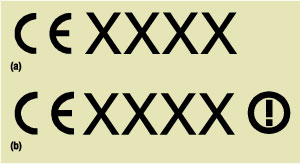
Figure 3:
(a) = harmonized frequency band product
label; (b) = a nonharmonized frequency band label
where
XXXX is the number of the notified body (if used)
Class 1 equipment, defined as equipment that
can be put into service in the entire European Union
|
Class 1 |
Equipment |
Comments |
|
1.1 |
ISDN
(ISDN Basic Rate, ISDN Primary Rate, ISDN U, Broadband ISDN ATM) |
Includes
TBR 3– and TBR 4–compliant equipment |
|
1.2 |
PSTN
(analog single line, analog multiline (with or without DDI), equipment
attached to Centrex interfaces or virtual private networks) |
Includes
TBR 21– and TBR 37–compliant equipment |
|
1.3 |
Leased
lines (2-W and 4-W analog [baseband], 2-W and 4-W analog [voice band],
digital, SDH, optical) |
Includes
TBR 12, TBR 13, TBR 15, TBR 17, TBR 24, and TBR 25–compliant equipment |
|
1.4 |
Wired
data equipment (X.21, X.25, Ethernet, token ring, token bus, TCP/IP, frame
relay) |
Includes
TBR 1– and TBR 2–compliant equipment |
|
1.5 |
Wired
interactive broadcast equipment (unswitched vision/sound, switched
vision/sound) |
— |
|
1.6 |
Telex
(single-line equipment, multiple-line equipment |
— |
|
1.7 |
Receive-only
radio equipment |
— |
|
1.8 |
Other
terminal equipment attached to fixed networks |
— |
|
1.9 |
GSM
handsets, including GSM 900, GSM 1800, GSM 1900, and (when it appears) GSM
450 |
Includes
TBR 19– and TBR 31–compliant equipment |
|
1.10 |
TFTS
equipment |
Includes
TBR 23–compliant equipment |
|
1.11 |
Land
mobile earth stations in the 1.5 and 1.6 GHz bands |
Includes
TBR 26–compliant equipment |
|
1.12 |
Land
mobile earth stations operating in the Ku-band |
Includes
TBR 27–compliant equipment |
|
1.13 |
TETRA
emergency equipment (non-DMO) |
Includes
TBR 35–compliant equipment |
|
1.14 |
Satellite
personal communication earth stations operating in the 1.6 and 2.4 GHz bands |
Includes
TBR 41–compliant equipment |
|
1.15 |
Satellite
personal communication earth stations operating in the 1.9 and 2.1 GHz bands |
Includes
TBR 42–compliant equipment |
|
1.16 |
Low-data-rate
land mobile earth stations in the 1.5 and 1.6 GHz bands |
Includes
TBR 44–compliant equipment |
|
1.17 |
Other
radio equipment, which only transmits under the control of a network |
— |
|
1.18 |
DECT
equipment |
Includes
TBR 6–compliant equipment |
Class 2 equipment, defined as equipment that
cannot be put into service or freely move throughout the entire European Union
for reasons stated in Articles 7.2 and 9.5 of the R&TTE Directive
|
Class 2 |
Equipment |
Comments |
|
2.0 |
Other |
— |
|
2.1 |
VSATs
in the C-band |
Includes
TBR 43–compliant equipment |
|
2.2 |
VSATs
in the Ku-band |
Includes
TBR 28–compliant equipment |
|
2.3 |
Satellite
news gathering earth stations |
Includes
TBR 30–compliant equipment |
|
2.4 |
TETRA
direct mode of operation |
— |
|
2.5 |
TETRAPOL |
— |
|
2.6 |
Private
mobile radio |
— |
|
2.7 |
Low-power
devices |
— |
|
2.8 |
Microwave
links |
— |
|
2.9 |
Fixed
radio links |
— |
|
2.10 |
Broadcast
transmitters |
— |
|
2.11 |
Maritime
radio equipment |
— |
|
2.12 |
Infrastructure
equipment (e.g., base stations) |
— |
|
2.13 |
Radio
equipment operating in amateur |
— |
Notifying Authorities
Not all of
Summary list of titles and references
of harmonised standards under Directive 1999/5/EC on R&TTE
This list replaces all the previous
lists published in the Official Journal of the European Union. The Commission
ensures the updating of this list.
However, this list does not have any legal validity; only publication in the
Official Journal produces legal affect.
|
Reference and title of the standard |
Reference of the superseded standard |
Date of cessation of presumption of conformity of the
superseded standard |
Article of
Directive 1999/5/EC |
|
EN 41003:1998 Particular
safety requirements for equipment to be connected to telecommunication
networks |
|
|
|
|
EN 50360:2001 Product
standard to demonstrate the compliance of mobile phones with the basic
restrictions related to human exposure to electromagnetic fields (300 MHz - 3
GHz) |
|
|
|
|
EN 50364:2001 Limitation of
human exposure to electromagnetic fields from devices operating in the
frequency range 0 Hz to 10 GHz, used in Electronic Article Surveillance
(EAS), Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) and similar applications |
|
|
|
|
EN 50371:2002 Generic
standard to demonstrate the compliance of low power electronic and electrical
apparatus with the basic restrictions related to human exposure to
electromagnetic fields (10 MHz - 300 GHz) - General public |
|
|
|
|
EN 50385:2002 Product
standard to demonstrate the compliance of radio base stations and fixed
terminal stations for wireless telecommunication systems with the basic
restrictions or the reference levels related to human exposure to radio
frequency electromagnetic fields (110 MHz - 40 GHz) - General public |
|
|
|
|
EN 50401:2006 Product
standard to demonstrate the compliance of fixed equipment for radio
transmission (110 MHz - 40 GHz) intended for use in wireless
telecommunication networks with the basic restrictions or the reference
levels related to general public exposure to radio frequency electromagnetic
fields, when put into service |
|
|
|
|
EN 55022:1998 Information
technology equipment - Radio disturbance characteristics - Limits and methods
of measurement (CISPR
22:1997 (Modified)) |
|
|
|
|
Amendment
A1:2000 to EN 55022:1998 (CISPR
22:1997/A1:2000) |
Note 3 |
1.10.2009 |
|
|
Amendment
A2:2003 to EN 55022:1998 (CISPR
22:1997/A2:2002) |
Note 3 |
1.10.2009 |
|
|
EN 55022:2006 Information
technology equipment - Radio disturbance characteristics - Limits and methods
of measurement (CISPR 22:2005
(Modified)) |
|
|
|
|
EN 55024:1998 Information
technology equipment - Immunity characteristics - Limits and methods of
measurement (CISPR
24:1997 (Modified)) |
|
|
|
|
Amendment
A1:2001 to EN 55024:1998 (CISPR
24:1997/A1:2001) |
Note 3 |
Date expired |
|
|
Amendment
A2:2003 to EN 55024:1998 (CISPR
24:1997/A2:2002) |
Note 3 |
Date expired |
|
|
EN 60065:2002 Audio, video
and similar electronic apparatus - Safety requirements (IEC
60065:2001 (Modified)) |
|
|
|
|
Amendment
A1:2006 to EN 60065:2002 (IEC 60065:2001/A1:2005
(Modified)) |
Note 3 |
1.12.2008 |
|
|
EN 60215:1989 Safety
requirements for radio transmitting equipment (IEC
60215:1987) |
|
|
|
|
Amendment
A1:1992 to EN 60215:1989 (IEC
60215:1987/A1:1990) |
Note 3 |
Date expired |
|
|
Amendment
A2:1994 to EN 60215:1989 (IEC
60215:1987/A2:1993) |
Note 3 |
Date expired |
|
|
EN 60825-1:1994 Safety of
laser products - Part 1: Equipment classification, requirements and user's
guide (IEC
60825-1:1993) |
|
|
|
|
Amendment
A1:2002 to EN 60825-1:1994 (IEC
60825-1:1993/A1:1997) |
EN
60825-1:1994/A11:1996Note 3 |
Date expired |
|
|
Amendment
A2:2001 to EN 60825-1:1994 (IEC
60825-1:1993/A2:2001) |
Note 3 |
Date expired |
|
|
EN 60825-2:2000 Safety of
laser products - Part 2: Safety of optical fibre communication systems (IEC
60825-2:2000) |
|
|
|
|
EN 60825-2:2004 Safety of
laser products - Part 2: Safety of optical fibre communication systems (OFCS)
(IEC
60825-2:2004) |
|
|
|
|
Amendment
A1:2007 to EN 60825-2:2004 (IEC
60825-2:2004/A1:2006) |
Note 3 |
1.2.2010 |
|
|
EN 60825-4:1997 Safety of
laser products - Part 4: Laser guards (IEC
60825-4:1997) |
|
|
|
|
Amendment
A1:2002 to EN 60825-4:1997 (IEC
60825-4:1997/A1:2002) |
Note 3 |
Date expired |
|
|
Amendment
A2:2003 to EN 60825-4:1997 (IEC
60825-4:1997/A2:2003) |
Note 3 |
Date expired |
|
|
EN 60825-4:2006 Safety of
laser products - Part 4: Laser guards (IEC
60825-4:2006) |
|
|
|
|
EN 60825-12:2004 Safety of
laser products - Part 12: Safety of free space optical communication systems
used for transmission of information (IEC
60825-12:2004) |
|
|
|
|
EN 60950-1:2001 Information
technology equipment - Safety - Part 1: General requirements (IEC
60950-1:2001 (Modified)) |
|
|
|
|
Amendment
A11:2004 to EN 60950-1:2001 |
Note 3 |
- |
|
|
EN 60950-1:2006 Information
technology equipment - Safety - Part 1: General requirements (IEC
60950-1:2005 (Modified)) |
|
|
|
|
EN 60950-22:2006 Information
technology equipment - Safety - Part 22: Equipment installed outdoors (IEC
60950-22:2005 (Modified)) |
|
|
|
|
EN 60950-23:2006 Information
technology equipment - Safety - Part 23: Large data storage equipment (IEC
60950-23:2005) |
|
|
|
|
EN 61000-3-2:2000 Electromagnetic
compatibility (EMC) - Part 3-2: Limits - Limits for harmonic current
emissions (equipment input current up to and including 16 A per phase) (IEC
61000-3-2:2000 (Modified)) |
|
|
|
|
Amendment
A2:2005 to EN 61000-3-2:2000 (IEC
61000-3-2:2000/A1:2001 |
Note 3 |
1.1.2008 |
|
|
EN 61000-3-2:2006 Electromagnetic
compatibility (EMC) - Part 3-2: Limits - Limits for harmonic current
emissions (equipment input current <= 16 A per phase) (IEC
61000-3-2:2005) |
|
|
|
|
EN 61000-3-3:1995 Electromagnetic
compatibility (EMC) - Part 3-3: Limits - Limitation of voltage changes,
voltage fluctuations and flicker in public low-voltage supply systems, for
equipment with rated current <= 16 A per phase and not subject to
conditional connection (IEC
61000-3-3:1994) |
|
|
|
|
Amendment
A1:2001 to EN 61000-3-3:1995 (IEC
61000-3-3:1994/A1:2001) |
Note 3 |
Date expired |
|
|
EN 61000-3-11:2000 Electromagnetic
compatibility (EMC) - Part 3-11: Limits - Limitation of voltage changes,
voltage fluctuations and flicker in public low-voltage supply systems -
Equipment with rated current <= 75 A and subject to conditional connection
(IEC
61000-3-11:2000) |
|
|
|
|
EN 61000-3-12:2005 Electromagnetic
compatibility (EMC) - Part 3-12: Limits - Limits for harmonic currents produced
by equipment connected to public low-voltage systems with input current >
16 A and <= 75 A per phase (IEC
61000-3-12:2004) |
|
|
|
|
EN 61000-6-1:2001 Electromagnetic
compatibility (EMC) - Part 6-1: Generic standards - Immunity for residential,
commercial and light-industrial environments (IEC
61000-6-1:1997 (Modified)) |
|
|
|
|
EN 61000-6-1:2007 Electromagnetic
compatibility (EMC) - Part 6-1: Generic standards - Immunity for residential,
commercial and light-industrial environments (IEC
61000-6-1:2005) |
|
|
|
|
EN 61000-6-2:2001 Electromagnetic
compatibility (EMC) - Part 6-2: Generic standards - Immunity for industrial
environments (IEC
61000-6-2:1999 (Modified)) |
|
|
|
|
EN 61000-6-2:2005 Electromagnetic
compatibility (EMC) - Part 6-2: Generic standards - Immunity for industrial
environments (IEC
61000-6-2:2005) |
|
|
|
|
EN 61000-6-3:2001 Electromagnetic
compatibility (EMC) - Part 6-3: Generic standards - Emission standard for
residential, commercial and light-industrial environments (CISPR/IEC
61000-6-3:1996 (Modified)) |
|
|
|
|
Amendment
A11:2004 to EN 61000-6-3:2001 |
Note 3 |
Date expired |
|
|
EN 61000-6-3:2007 Electromagnetic
compatibility (EMC) - Part 6-3: Generic standards - Emission standard for
residential, commercial and light-industrial environments (IEC
61000-6-3:2006) |
|
|
|
|
EN 61000-6-4:2001 Electromagnetic
compatibility (EMC) - Part 6-4: Generic standards - Emission standard for
industrial environments (IEC
61000-6-4:1997 (Modified)) |
|
|
|
|
EN 61000-6-4:2007 Electromagnetic
compatibility (EMC) - Part 6-4: Generic standards - Emission standard for
industrial environments (IEC
61000-6-4:2006) |
|
|
|
|
EN 300 065-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Narrow-band direct-printing
telegraph equipment for receiving meteorological or navigational information
(NAVTEX); Part 2: Harmonised EN covering essential requirements of Article
3(2)(2) of the R&TTE directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 065-3 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Narrow-band direct-printing
telegraph equipment for receiving meteorological or navigational information
(NAVTEX); Part 3: Harmonised EN covering essential requirements of Article
(3)(3)(e) of the R&TTE directive |
|
|
Article 3(3) |
|
EN 300 086-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Land Mobile Service; Radio
equipment with an internal or external RF connector intended primarily for
analogue speech; Part 2: Harmonised EN covering essential requirements under
Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
ETS 300 086/A2 (02-1997) |
Date expired (31.8.2002) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 113-2 V1.3.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Land mobile service; Radio
equipment intended for the transmission of data (and/or speech) using
constant or non-constant envelope modulation and having an antenna connector;
Part 2: Harmonised EN covering essential requirements under Article 3(2) of
the R&TTE Directive |
EN 300 113-2 V1.2.1 |
Date expired (28.2.2007) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 113-2 V1.4.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Land mobile service; Radio
equipment intended for the transmission of data (and/or speech) using
constant or non-constant envelope modulation and having an antenna connector;
Part 2: Harmonised EN covering essential requirements of Article 3(2) of the
R&TTE Directive |
EN 300 113-2 V1.3.1 |
31.3.2009 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 135-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Angle-modulated Citizens Band
radio equipment (CEPT PR 27 Radio Equipment); Part 2: Harmonised EN covering
essential requirements under Article 3(2) of R&TTE Directive |
ETS 300 135/A1:1997 |
Date expired (30.4.2001) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 152-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Maritime Emergency Position
Indicating Radio Beacons (EPIRBs) intended for use on the frequency 121,5 MHz
or the frequencies 121,5 MHz and 243 MHz for homing purposes only; Part 2:
Harmonised EN under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 152-3 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Maritime Emergency Position
Indicating Radio Beacons (EPIRBs) intended for use on the frequency 121,5 MHz
or the frequencies 121,5 MHz and 243 MHz for homing purposes only; Part 3:
Harmonised EN under Article 3(3)e of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(3) |
|
EN 300 162-2 V1.1.2 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Radiotelephone transmitters
and receivers for the maritime mobile service operating in VHF bands; Part 2:
Harmonised EN covering essential requirements under Article 3(2) of the
R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 162-2 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Radiotelephone transmitters
and receivers for the maritime mobile service operating in VHF bands; Part 2:
Harmonised EN covering essential requirements of Article 3(2) of the
R&TTE Directive |
EN 300 162-2 V1.1.2 |
31.8.2008 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 162-3 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Radiotelephone transmitters
and receivers for the maritime mobile service operating in VHF bands; Part 3:
Harmonised EN covering essential requirements of Article 3(3)e of the
R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(3) |
|
EN 300 162-3 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Radiotelephone transmitters
and receivers for the maritime mobile service operating in VHF bands; Part 3:
Harmonised EN covering essential requirements of Article 3(3) (e) of the
R&TTE Directive |
EN 300 162-3 V1.1.1 |
31.8.2008 |
Article 3(3) |
|
EN 300 219-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Land Mobile Service; Radio
equipment with an internal or external RF connector intended primarily for
analogue speech; Part 2: Harmonised EN covering essential requirements under
Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 220-2 V2.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Short Range Devices (SRD);
Radio equipment to be used in the 25 MHz to 1 000 MHz frequency range with
power levels ranging up to 500 mW; Part 2: Harmonised EN covering essential
requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 300 220-3 V.1.1.1 |
31.12.2007 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 220-2 V2.1.2 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Short Range Devices (SRD);
Radio equipment to be used in the 25 MHz to 1 000 MHz frequency range with
power levels ranging up to 500 mW; Part 2: Harmonised EN covering essential
requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 300 220-2 V2.1.1 |
31.3.2009 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 220-3 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Short Range Devices (SRD);
Radio equipment to be used in the 25 MHz to 1 000 MHz frequency range with
power levels ranging up to 500 mW; Part 3: Harmonised EN covering essential
requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 224-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); On-site paging service; Part
2: Harmonised EN under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 296-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Land Mobile Service; Radio
equipment using integral antennas intended primarily for analogue speech;
Part 2: Harmonised EN covering essential requirements under Article 3(2) of
the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 328 V1.6.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio Spectrum Matters (ERM); Wideband Transmission
systems; Data transmission equipment operating in the 2,4 GHz ISM band and
using spread spectrum modulation techniques; Harmonised EN covering essential
requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 300 328 V1.5.1 |
Date expired (31.8.2006) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 328 V1.7.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Wideband transmission
systems; Data transmission equipment operating in the 2,4 GHz ISM band and
using wide band modulation techniques; Harmonised EN covering essential
requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 300 328 V1.6.1 |
30.6.2008 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 330-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Short Range Devices (SRD);
Radio equipment in the frequency range 9 kHz to 25 MHz and inductive loop
systems in the frequency range 9 kHz to 30 MHz; Part 2: Harmonised EN under
Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 330-2 V1.3.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Short Range Devices (SRD);
Radio equipment in the frequency range 9 kHz to 25 MHz and inductive loop
systems in the frequency range 9 kHz to 30 MHz; Part 2: Harmonised EN under
Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 300 330-2 V1.1.1 |
31.12.2007 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 341-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Land Mobile service (RP 02);
Radio equipment using an integral antenna transmitting signals to initiate a
specific response in the receiver; Part 2: Harmonised EN under Article 3(2)
of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 373-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Maritime mobile transmitters
and receivers for use in the MF and HF bands Part 2: Harmonised EN covering
essential requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 373-3 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Maritime mobile transmitters
and receivers for use in the MF and HF bands Part 3: Harmonised EN covering
essential requirements of Article 3(3)(e) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(3) |
|
EN 300 390-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Land Mobile Service; Radio
equipment intended for the transmission of data (and speech) and using an
integral antenna; Part 2: Harmonised EN covering essential requirements under
Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
ETS 300 390/A1:1997 |
Date expired (30.4.2001) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 422-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Wireless microphones in the
25 MHz to 3 GHz frequency range; Part 2: Harmonised EN under Article 3(2) of
the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 433-2 V1.1.2 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Land Mobile Service; Double
Side Band (DSB) and/or Single Side Band (SSB) Amplitude modulated Citizen's
Band radio Equipment; Part 2: Harmonised EN covering essential requirements
under Article 3(2) of R&TTE Directive |
EN 300 433-2 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.9.2002) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 440-2 V1.1.2 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Short range devices; Radio
equipment to be used in the 1 GHz to 40 GHz frequency range; Part 2:
Harmonised EN under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 300 440-2 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.6.2007) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 454-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Wide band audio links; Part
2: Harmonised EN under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 471-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Land Mobile Service; Access
protocol, occupation rules and corresponding technical characteristics of radio
equipment for the transmission of data on shared channels; Part 2: Harmonised
EN covering essential requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE
Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 674-2-1 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Road Transport and Traffic
Telematics (RTTT); Dedicated Short Range Communication (DSRC) transmission
equipment (500 kbit/s / 250 kbit/s) operating in the 5,8 GHz Industrial,
Scientific and Medical (ISM) band; Part 2: Harmonised EN under Article 3(2)
of the R&TTE Directive; Sub-part 1: Requirements for the Road Side Units
(RSU) |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 674-2-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Road Transport and Traffic
Telematics (RTTT); Dedicated Short Range Communication (DSRC) transmission
equipment (500 kbit/s / 250 kbit/s) operating in the 5,8 GHz Industrial,
Scientific and Medical (ISM) band; Part 2: Harmonised EN under Article 3(2)
of the R&TTE Directive; Sub-part 2: Requirements for the On-Board Units (OBU)
|
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 698-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio Spectrum Matters (ERM); Radio telephone transmitters
and receivers for the maritime mobile service operating in the VHF bands used
on inland waterways; Part 2: Harmonised EN under Article 3(2) of the
R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 698-3 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio Spectrum Matters (ERM); Radio telephone transmitters
and receivers for the maritime mobile service operating in the VHF bands used
on inland waterways; Part 3: Harmonised EN under Article 3(3)e of the
R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(3) |
|
EN 300 718-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Avalanche Beacons;
Transmitter-receiver systems; Part 2: Harmonised EN covering essential
requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 718-3 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Avalanche beacons;
Transmitter-receiver systems; Part 3: Harmonised EN covering the essential
requirements of Article 3(3)e of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 300 718-3 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.11.2005) |
Article 3(3) |
|
EN 300 720-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio Spectrum Matters (ERM); Ultra-High Frequency (UHF)
on-board communications systems and equipment; Part 2: Harmonised EN under
Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 300 761-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Short Range Devices (SRD);
Automatic Vehicle Identification (AVI) for railways operating in the 2,45 GHz
frequency range; Part 2: Harmonised standard covering essential requirements
under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 025-2 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); VHF radiotelephone equipment
for general communications and associated equipment for Class ‘D’ Digital
Selective Calling (DSC); Part 2: Harmonised EN under Article 3(2) of the
R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 025-2 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.6.2006) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 025-2 V1.3.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); VHF radiotelephone equipment
for general communications and associated equipment for class ‘D’ Digital
Selective Calling (DSC); Part 2: Harmonised EN under Article 3(2) of the
R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 025-2 V1.2.1 |
31.10.2008 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 025-3 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); VHF radiotelephone equipment
for general communications and associated equipment for Class ‘D’ Digital
Selective Calling (DSC); Part 3: Harmonised EN under Article 3(3)e of the
R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 025-3 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.6.2006) |
Article 3(3) |
|
EN 301 025-3 V1.3.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); VHF radiotelephone equipment
for general communications and associated equipment for Class ‘D’ Digital
Selective Calling (DSC); Part 3: Harmonised EN under Article 3(3)e of the
R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 025-3 V1.2.1 |
31.10.2008 |
Article 3(3) |
|
EN 301 091-2 V.1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Road Transport and Traffic
Telematics (RTTT); Radar equipment operating in the 76 GHz to 77 GHz; Part 2:
Harmonised EN covering essential requirements of Article 3(2) of the
R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 091-2 V1.3.2 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Short Range Devices; Road
Transport and Traffic Telematics (RTTT); Radar equipment operating in the 76
GHz to 77 GHz; Part 2: Harmonised EN covering essential requirements of
Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 091-2 V1.2.1 |
30.6.2008 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 166-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Land mobile service;
Technical characteristics and test conditions for radio equipment for
analogue and/or digital communication (speech and/or data) and operating on
narrowband channels and having an antenna connector; Part 2: Harmonised EN
covering essential requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive
|
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 166-2 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Land Mobile Service; Radio
equipment for analogue and/or digital communication (speech and/or data) and
operating on narrow band channels and having an antenna connector; Part 2:
Harmonised EN covering essential requirements of Article 3(2) of the
R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 166-2 V1.1.1 |
31.3.2009 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 178-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Portable Very High Frequency
(VHF) radiotelephone equipment for the maritime mobile service operating in
the VHF bands (for non-GMDSS applications only); Part 2: Harmonised EN under
Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 178-2 V1.2.2 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Portable Very High Frequency
(VHF) radiotelephone equipment for the maritime mobile service operating in
the VHF bands (for non-GMDSS applications only); Part 2: Harmonised EN under
Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 178-2 V1.1.1 |
31.10.2008 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 357-2 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Cordless audio devices in the
range 25 MHz to 2000 MHz; Consumer radio microphones and in-ear monitoring
systems operating in the CEPT harmonized band 863 MHz to 865 MHz; Part 2:
Harmonised EN under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 357 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (31.3.2003) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 357-2 V1.3.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Cordless audio devices in the
range 25 MHz to 2 000 MHz; Consumer radio microphones and in-ear monitoring
systems operating in the CEPT harmonized band 863 MHz to 865 MHz; Part 2:
Harmonised EN under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 357-2 V1.2.1 |
30.4.2008 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 360 V1.1.3 Satellite
Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Harmonised EN for Satellite User Terminals
(SUT) transmitting towards satellites in geostationary orbit in the 27,5 to
29,5 GHz frequency bands covering essential requirements under Article 3(2)
of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 360 V1.2.1 Satellite
Earth Stations and Systems (SES);Harmonised EN for Satellite Interactive
Terminals (SIT) and Satellite User Terminals (SUT) transmitting towards
geostationary satellites in the 27,5 GHz to 29,5 GHz frequency bands covering
essential requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 360 V1.1.3 |
30.11.2007 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 406 V1.5.1 Digital
Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications (DECT); Harmonised EN for Digital
Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications (DECT) covering essential requirements
under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive; Generic radio |
EN 301 406 V1.4.1 |
Date expired (31.3.2005) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 419-1 V4.0.1 Digital
cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2); Attachment requirements for
Global System for Mobile communications (GSM); Part 1: Mobile stations in the
GSM 900 and DCS 1 800 bands; Access (GSM 13.01 version 4.0.1) (applicable
parts: 12.1.1, 12.1.2, 12.2.1, 12.2.2, 13.1, 13.2, 13.3-1, 13.4, 14.1.1.2,
14.1.2.2, 14.3, 14.4.1, 14.5.1, 14.6.1, 14.7.1, 19.1, 19.2, 19.3, 20.1, 20.2,
20.3, 20.4, 20.5, 20.6, 20.7, 20.8, 20.9, 20.10, 20.11, 20.12, 20.13, 20.15,
20.16, 20.20.1, 20.20.2, 21.1, 21.2, 21.3.1, 21.3.2, 21.4, 22.1, 25.2.1.1.4,
25.2.1.2.3, 25.2.1.2.4, 25.2.3, 26.2.1.1, 26.2.1.2, 26.2.1.3, 26.2.2,
26.6.1.1, 26.6.1.2, 26.6.13.10, 26.6.13.3, 26.6.13.5, 26.6.13.6, 26.6.13.8,
26.6.13.9, 26.7.4.6, 26.7.5.7.1, 26.8.1.2.6.6, 26.8.1.3.5.2, 26.8.2.1, 26.8.2.2,
26.8.2.3, 26.8.3, 26.9.2, 26.9.3, 26.9.4, 26.9.5, 26.10.2.2, 26.10.2.3,
26.10.2.4.1, 26.10.2.4.2, 26.11.2.1, 26.12.1, 26.12.2.1, 26.12.3, 26.12.4,
27.6, 27.7, 31.6.1.1, 34.2.1, 34.2.2, 34.2.3) |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 419-2 V5.1.1 Digital
cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Attachment requirements for
Global System for |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 419-3 V5.0.2 Digital
cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Attachment requirements for
Global System for Mobile communications (GSM); Advanced Speech Call Items
(ASCI); Mobile Stations; Access (GSM 13.68 version 5.0.2 Release 1996)
(applicable parts: 26.14.5.2, 26.14.7.3, 26.14.8.1) |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 419-7 V5.0.2 Digital
cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Attachment requirements for
Global System for Mobile communications (GSM); Railways Band (R-GSM); Mobile
Stations; Access (GSM 13.67 version 5.0.2) (applicable parts: 12.3.1, 12.3.2,
12.4.1, 12.4.2, 13.9, 14.7.3, 20.21.1, 20.21.2, 20.21.3, 20.21.4, 20.21.5,
20.21.6, 20.21.7, 20.21.8, 20.21.9, 20.21.10, 20.21.11, 20.21.12, 20.21.13,
20.21.15, 20.21.16, 20.21.18, 26.10.2.2, 26.10.2.3, 26.10.2.4.1, 26.10.2.4.2)
|
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 423 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
Compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Harmonised Standard for the
Terrestrial Flight Telecommunications System under Article 3(2) of the
R&TTE Directive |
TBR 23: 1998 |
Date expired (30.9.2002) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 426 V1.2.1 Satellite
Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Harmonised EN for low data rate Land Mobile
satellite Earth Stations (LMES) operating in the 1,5/1,6 GHz frequency bands
covering essential requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive
|
EN 301 426 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.6.2002) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 427 V1.2.1 Satellite
Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Harmonised EN for Low data rate Mobile
satellite Earth Stations (MESs) except aeronautical mobile satellite earth
stations, operating in the 11/12/14 GHz frequency bands covering essential
requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE directive |
EN 301 427 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (31.8.2003) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 428 V1.3.1 Satellite
Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Harmonised EN for Very Small Aperture
Terminal (VSAT); Transmit-only, transmit/receive or receive-only satellite
earth stations operating in the 11/12/14 GHz frequency bands covering
essential requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE directive |
EN 301 428 V1.2.1 |
Date expired (30.6.2007) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 430 V1.1.1 Satellite
Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Harmonised EN for Satellite News Gathering
Transportable Earth Stations (SNG TES) operating in the 11-12/13-14 GHz
frequency bands covering essential requirements under Article 3(2) of the
R&TTE Directive |
TBR 30: 1998 |
Date expired (31.1.2001) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 441 V1.1.1 Satellite
Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Harmonised EN for Mobile Earth Stations
(MESs), including handheld earth stations, for Satellite Personal
Communications Networks (S-PCN) in the 1,6/2,4 GHz bands under the Mobile
Satellite Service (MSS) covering essential requirements under Article 3(2) of
the R&TTE Directive |
TBR 41: 1998 |
Date expired (31.1.2001) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 442 V1.1.1 Satellite
Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Harmonised EN for Mobile Earth Stations
(MESs), including handheld earth stations, for Satellite Personal
Communications Networks (S-PCN) in the 2,0 GHz bands under the Mobile
Satellite Service (MSS) covering essential requirements under Article 3(2) of
the R&TTE Directive |
TBR 42: 1998 |
Date expired (31.1.2001) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 443 V1.2.1 Satellite
Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Harmonised EN for Very Small Aperture
Terminal (VSAT); Transmit-only, transmit-and-receive, receive-only satellite
earth stations operating in the 4 GHz and 6 GHz frequency bands covering
essential requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 443 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.11.2001) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 443 V1.3.1 Satellite
Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Harmonised EN for Very Small Aperture
Terminal (VSAT); Transmit only, transmit and receive, receive only satellite
earth stations operating in the 4 GHz and 6 GHz frequency bands covering
essential requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 443 V1.2.1 |
30.11.2007 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 444 V1.1.1 Satellite
Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Harmonised EN for Land Mobile Earth
Stations (LMES) operating in the 1,5 GHz and 1,6 GHz bands providing voice
and/or data communications covering essential requirements under Article 3(2)
of the R&TTE Directive |
TBR 44: 1998 |
Date expired (31.1.2001) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 449 V1.1.1 Electomagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Harmonised EN for CDMA spread
spectrum base stations operating in the 450 MHz cellular band (CDMA 450) and
410, 450 and 870 MHz PAMR bands (CDMA-PAMR) covering essential requirements
of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 459 V1.2.1 Satellite
Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Harmonised EN for Satellite Interactive
Terminals (SIT) and Satellite User Terminals (SUT) transmitting towards
satellites in geostationary orbit in the 29,5 to 30,0 GHz frequency bands
covering essential requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE directive
|
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 459 V1.3.1 Satellite
Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Harmonised EN for Satellite Interactive
Terminals (SIT) and Satellite User Terminals (SUT) transmitting towards
satellites in geostationary orbit in the 29,5 to 30,0 GHz frequency bands
covering essential requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE directive
|
EN 301 459 V.1.2.1 |
31.12.2008 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 459 V1.4.1 Satellite
Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Harmonised EN for Satellite Interactive
Terminals (SIT) and Satellite User Terminals (SUT) transmitting towards
satellites in geostationary orbit in the 29,5 GHz to 30,0 GHz frequency bands
covering essential requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive
|
EN 301 459 V1.3.1 |
31.3.2009 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 489-01 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 1: Common technical
requirements |
|
|
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-01 V1.3.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 1: Common technical
requirements |
EN 301 489-01 V1.2.1 |
31.8.2007 |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-01 V1.4.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 1: Common technical
requirements |
EN 301 489-01 V1.2.1 & V1.3.1 |
31.8.2007 |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-01 V1.5.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 1: Common technical
requirements |
EN 301 489-01 V1.4.1 |
11.8.2008 |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-01 V1.6.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); ElectromagneticCompatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 1: Common technical
requirements |
EN 301 489-01 V1.5.1 |
30.11.2008 |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-02 V1.3.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 2: Specific conditions
for radio paging equipment |
EN 301 489-02 V1.2.1 |
Date expired (30.11.2005) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-03 V1.4.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 3: Specific conditions
for Short-Range Devices (SRD) operating on frequencies between 9 kHz and 40
GHz |
EN 301 489-03 V1.3.1 |
Date expired (30.11.2005) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-04 V1.3.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 4: Specific conditions
for fixed radio links and ancillary equipment and services |
EN 301 489-04 V1.2.1 |
Date expired (30.11.2005) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-05 V1.3.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 5: Specific conditions
for |
EN 301 489-05 V1.2.1 |
Date expired (30.11.2005) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-06 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 6: Specific conditions
for Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications (DECT) equipment |
EN 301 489-06 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.11.2005) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-07 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 7: Specific conditions
for mobile and portable radio and ancillary equipment of digital cellular
radio telecommunications systems (GSM and DCS) |
EN 301 489-07 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.11.2005) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-07 V1.3.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 7: Specific conditions
for mobile and portable radio and ancillary equipment of digital cellular
radio telecommunications systems (GSM and DCS) |
EN 301 489-07 V1.2.1 |
31.1.2009 |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-08 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 8: Specific conditions
for GSM base stations |
EN 301 489-08 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.11.2005) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-09 V1.3.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 9: Specific conditions
for wireless microphones, similar Radio Frequency (RF) audio link equipment,
cordless audio and in-ear monitoring devices |
EN 301 489-09 V1.2.1 |
Date expired (30.11.2005) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-10 V1.3.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 10: Specific conditions
for First (CT1 and CT1+) and Second Generation Cordless Telephone (CT2)
equipment |
EN 301 489-10 V1.2.1 |
Date expired (30.11.2005) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-11 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 11: Specific conditions
for terrestrial sound broadcasting service transmitters |
EN 301 489-11 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.11.2005) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-11 V1.3.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 11: Specific conditions
for terrestrial sound broadcasting service transmitters |
EN 301 489-11 V1.2.1 |
30.11.2007 |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-12 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 12: Specific conditions
for Very Small Aperture Terminal, Satellite Interactive Earth Stations
operated in the frequency ranges between 4 GHz and 30 GHz in the Fixed
Satellite Service (FSS) |
EN 301 489-12 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (31.7.2006) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-13 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 13: Specific conditions
for Citizens' Band (CB) radio and ancillary equipment (speech and non-speech)
|
EN 301 489-13 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.11.2005) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-14 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 14: Specific conditions
for analogue and digital terrestrial TV broadcasting service transmitters |
EN 301 489-14 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (31.7.2006) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-15 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 15: Specific conditions
for commercially available amateur radio equipment |
EN 301 489-15 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.11.2005) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-16 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 16: Specific conditions
for analogue cellular radio communications equipment, mobile and portable |
EN 301 489-16 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.11.2005) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-17 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 17: Specific conditions
for 2,4 GHz wideband transmission systems and 5 GHz high performance RLAN
equipment |
EN 301 489-17 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.11.2005) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-18 V1.3.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 18: Specific conditions
for Terrestrial Trunked Radio (TETRA) equipment |
EN 301 489-18 V1.2.1 |
Date expired (30.11.2005) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-19 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 19: Specific conditions
for Receive Only Mobile Earth Stations (ROMES) operating in the 1,5 GHz band
providing data communication |
EN 301 489-19 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.11.2005) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-20 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 20: Specific conditions
for Mobile Earth Stations (MES) used in the Mobile Satellite Services (MSS) |
EN 301 489-20 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.11.2005) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-22 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 22: Specific
requirements for ground-based VHF aeronautical mobile and fixed radio
equipment |
EN 301 489-22 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.11.2005) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-22 V1.3.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 22: Specific
requirements for ground-based VHF aeronautical mobile and fixed radio
equipment |
EN 301 489-22 V1.2.1 |
Date expired (28.2.2007) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-23 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio Spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 23: Specific conditions
for IMT-2000 CDMA Direct Spread (UTRA) Base Station (BS) radio, repeater and
ancillary equipment |
EN 301 489-23 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.11.2005) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-24 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio Spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 24: Specific conditions
for IMT-2000 CDMA Direct Spread (UTRA) for |
EN 301 489-24 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.11.2005) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-24 V1.3.1 (10-2005) Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 24: Specific conditions
for IMT-2000 CDMA Direct Spread (UTRA) for |
EN 301 489-24 V1.2.1 |
31.1.2009 |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-25 V2.0.0 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio Spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 25: Specific conditions
for IMT-2000 CDMA Multi-carrier Mobile Stations and ancillary equipment |
|
|
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-25 V2.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio Spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 25: Specific conditions
for IMT-2000 CDMA Multi-carrier Mobile Stations and ancillary equipment |
EN 301 489-25 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (31.7.2006) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-25 V2.3.2 (7-2005) Electromagnetic
compatibility and radio spectrum matters (ERM); Electromagnetic compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 25: Specific conditions
for CDMA 1x Spread Spectrum Mobile Stations and ancillary equipment |
EN 301 489-25 V2.2.1 |
Date expired (30.4.2007) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-26 V2.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio Spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 26: Specific conditions
for IMT-2000 CDMA Multi-carrier Base Stations and ancillary equipment |
EN 301 489-26 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (31.7.2006) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-26 V2.3.2 Electromagnetic
compatibility and radio spectrum matters (ERM); Electromagnetic compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 26: Specific conditions
for CDMA 1x spread spectrum base stations, repeaters and ancillary equipment |
EN 301 489-26 V2.2.1 |
Date expired (30.4.2007) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-27 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 27: Specific conditions
for Ultra Low Power Active Medical Implants (ULP-AMI) and related peripheral
devices (ULP-AMI-P) |
|
|
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-28 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio Spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 28: Specific conditions
for wireless digital video links |
|
|
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-31 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 31: EMC for radio
equipment in the 9 to 315 kHz band for Ultra Low Power Active Medical
Implants (ULP-AMI) and related peripheral devices (ULP-AMI-P) |
|
|
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 489-32 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 32: Ground and
Wall-Probing Radar applications |
|
|
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 502 V8.1.2 Harmonised EN
for Global System for |
EN 301 502 V7.0.1 |
Date expired (30.4.2002) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 511 V9.0.2 Global System
for Mobile communications (GSM); Harmonised standard for mobile stations in
the GSM 900 and DCS 1800 bands covering essential requirements under Article
3(2) of the R&TTE directive (1999/5/EC) |
EN 301 511 V7.0.1 |
Date expired (30.6.2004) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 526 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Harmonised EN for CDMA spread
spectrum mobile stations operating in the 450 MHz cellular band (CDMA 450)
and 410, 450 and 870 MHz PAMR bands (CDMA-PAMR) covering essential
requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 681 V1.3.2 Satellite
Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Harmonised EN for Mobile Earth Stations
(MESs) of Geostationary mobile satellite systems, including handheld earth
stations, for Satellite Personal Communications Networks (S-PCN) in the
1,5/1,6 GHz bands under the Mobile Satellite Service (MSS) covering essential
requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE directive |
EN 301 681 V1.2.1 |
Date expired (31.3.2006) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 721 V1.2.1 Satellite
Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Harmonised EN for Mobile Earth Stations
(MES) providing Low Bit Rate Data Communications (LBRDC) using Low Earth
Orbiting (LEO) satellites operating below 1 GHz covering essential
requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 721 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (31.3.2002) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 751 V1.2.1 Fixed Radio
Systems; Point-to-Point equipment and antennas; Generic harmonised standard
for Point-to-Point digital fixed radio systems and antennas covering the
essential requirements under Article 3(2) of the 1999/05/EC Directive |
EN 301 751 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.4.2005) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 753 V1.2.1 Fixed Radio
Systems; Multipoint equipment and antennas; Generic harmonized standard for
multipoint digital fixed radio systems and antennas covering the essential
requirements under Article 3(2) of the Directive 1999/5/EC |
EN 301 753 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (28.2.2006) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 783-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio Spectrum Matters (ERM); Land Mobile Service;
Commercially available amateur radio equipment; Part 2: Harmonised EN
covering essential requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive
|
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 796 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Harmonised EN for CT1 and
CT1+ cordless telephone equipment covering essential requirements under
Article 3(2) of the R&TTE directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 797 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Harmonised EN for CT2
cordless telephone equipment covering essential requirements under Article
3(2) of the R&TTE directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 839-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Radio equipment in the
frequency range 402 MHz to 405 MHz for Ultra Low Power Active Medical
Implants and Accessories; Part 2: Harmonised EN covering essential
requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 839-2 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Short Range Devices (SRD);
Ultra Low Power Active Medical Implants (ULP-AMI) and Peripherals (ULP-AMI-P)
operating in the frequency range 402 MHz to 405 MHz; Part 2: Harmonised EN
covering essential requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 839-2 V1.1.1 |
31.3.2009 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 840-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Digital wireless microphones
operating in the CEPT harmonized band 1785 MHz to 1 800 MHz; Part 2:
Harmonised EN under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 843-1 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for marine radio equipment and services; Part 1: Common
technical requirements |
EN 301 843-1 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (31.3.2006) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 843-4 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for marine radio equipment and services; Part 4: Specific
conditions for Narrow-Band Direct-Printing (NBDP) NAVTEX receivers |
EN 301 843-4 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (31.3.2006) |
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 843-5 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for marine radio equipment and services; Part 5: Specific
conditions for MF/HF radiotelephone transmitters and receivers |
|
|
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 843-6 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) standard for marine radio equipment and services; Part 6: Specific
conditions for Earth Stations on board Vessels operating in frequency bands
above 3 GHz |
|
|
Article 3(1)(b) |
|
EN 301 893 V1.2.3 Broadband
Radio Access Networks (BRAN); 5 GHz high performance RLAN; Harmonised EN
covering essential requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 893 V1.3.1 Broadband
Radio Access Networks (BRAN); 5 GHz high performance RLAN; Harmonised EN
covering essential requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 893 V1.2.3 |
31.3.2008 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 893 V1.4.1 Broadband
Radio Access Networks (BRAN); 5 GHz high performance RLAN; Harmonised EN
covering essential requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 893 V1.3.1 |
31.3.2009 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 908-01 V2.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Base Stations (BS) and User
Equipment (UE) for IMT-2000 Third Generation cellular networks; Part 1:
Harmonised EN for IMT-2000, introduction and common requirements of Article
3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 908-01 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (31.1.2006) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 908-01 V3.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Base Stations (BS) and User
Equipment (UE) for IMT-2000 Third Generation cellular networks; Part 1:
Harmonised EN for IMT-2000, introduction and common requirements of Article
3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 908-01 V2.2.1 |
31.1.2009 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 908-02 V2.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Base Stations (BS) and User
Equipment (UE) for IMT-2000 Third Generation cellular networks; Part 2:
Harmonised EN for IMT-2000, CDMA Direct Spread (UTRA FDD) (UE) covering
essential requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 908-02 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (31.1.2006) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 908-02 V3.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Base Stations (BS) and User
Equipment (UE) for IMT-2000 Third Generation cellular networks; Part 2:
Harmonised EN for IMT-2000, CDMA Direct Spread (UTRA FDD) (UE) covering
essential requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 908-02 V2.2.1 |
31.1.2009 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 908-03 V2.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Base Stations (BS) and User
Equipment (UE) for IMT-2000 Third Generation cellular networks; Part 3:
Harmonised EN for IMT-2000, CDMA Direct Spread (UTRA FDD) (BS) covering
essential requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 908-03 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (31.1.2006) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 908-03 V3.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Base Stations (BS) and User
Equipment (UE) for IMT-2000 Third Generation cellular networks; Part 3:
Harmonised EN for IMT-2000, CDMA Direct Spread (UTRA FDD) (BS) covering
essential requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 908-03 V2.2.1 |
31.1.2009 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 908-04 V2.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Base Stations (BS) and User
Equipment (UE) for IMT-2000 Third Generation cellular networks; Part 4:
Harmonised EN for IMT-2000, CDMA Multi-Carrier (cdma2000) (UE) covering the
essential requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 908-04 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (31.1.2006) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 908-05 V2.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Base Stations (BS), Repeaters
and User Equipment (UE) for IMT-2000 Third-Generation cellular networks; Part
5: Harmonised standard for IMT-2000, CDMA Multi-Carrier (cdma2000) (BS and
Repeaters) covering essential requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE
Directive |
EN 301 908-05 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (31.1.2006) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 908-06 V2.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Base Stations (BS), Repeaters
and User Equipment (UE) for IMT-2000 Third-Generation cellular networks; Part
6: Harmonised EN for IMT-2000, CDMA TDD (UTRA TDD) (UE) covering essential
requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 908-06 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (31.1.2006) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 908-07 V2.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Base Stations (BS) and User
Equipment (UE) for IMT-2000 Third Generation cellular networks; Part 7:
Harmonised EN for IMT-2000, CDMA TDD (UTRA TDD) (BS) covering
essentialessential requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 908-07 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (31.1.2006) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 908-07 V2.2.2 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Base Stations (BS), Repeaters
and User Equipment (UE) for IMT-2000 Third-Generation cellular networks; Part
7: Harmonised EN for IMT-2000, CDMA TDD (UTRA TDD) (BS) covering essential
requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 908-07 V3.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Base Stations (BS) and User
Equipment (UE) for IMT-2000 Third Generation cellular networks; Part 7:
Harmonised EN for IMT-2000, CDMA TDD (UTRA TDD) (BS) covering
essentialessential requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 908-07 V2.2.2 & EN 301 908-07 V2.2.1 |
31.1.2009 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 908-08 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Base Stations (BS) and User
Equipment (UE) for IMT-2000 Third Generation cellular networks; Part 8:
Harmonised EN for IMT-2000, TDMA Single-Carrier (UWC 136) (UE) covering
essentialessential requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 908-09 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Base Stations (BS) and User
Equipment (UE) for IMT-2000 Third Generation cellular networks; Part 9:
Harmonised EN for IMT-2000, TDMA Single-Carrier (UWC 136) (BS) covering
essential requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 908-10 V2.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Base Stations (BS) and User
Equipment (UE) for IMT-2000 Third Generation cellular networks; Part 10:
Harmonised EN for IMT-2000, FDMA/TDMA (DECT) covering essential requirements
of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 908-10 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.9.2005) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 908-11 V.2.3.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Base Stations (BS), Repeaters
and User Equipment (UE) for IMT-2000 Third Generation cellular Networks; Part
11: Harmonised EN for IMT-2000, CDMA Direct Spread (UTRA FDD) (Repeaters)
covering the essential requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE
Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 908-11 V3.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Base Stations (BS), Repeaters
and User Equipment (UE) for IMT-2000 Third-Generation cellular networks; Part
11: Harmonised EN for IMT-2000, CDMA Direct Spread (UTRA FDD) (Repeaters)
covering essential requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 301 908-11 V2.3.1 |
31.1.2009 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 929-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); VHF transmitters and
receivers as Coast Stations for GMDSS and other applications in the maritime
mobile services; Part 2: Harmonised EN under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE
Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 929-2 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); VHF transmitters and
receivers as Coast Stations for GMDSS and other applications in the maritime
mobile services; Part 2: Harmonised EN under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE
Directive |
EN 301 929-2 V1.1.1 |
30.11.2008 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 301 997-2 V1.1.1 Transmission
and Multiplexing (TM); Multipoint equipment; Radio equipment for use in
Multimedia Wireless Systems (MWS) in the frequency band 40,5 GHz to 43,5 GHz;
Part 2: Harmonised EN covering essential requirements under Article 3(2) of
the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 017-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Transmitting equipment for
the Amplitude Modulated (AM) sound broadcasting service; Part 2: Harmonised
EN covering essential requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE
Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 018-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
Compatibility and Radio Spectrum Matters (ERM); Transmitting equipment for
the Frequency Modulated (FM) radio broadcast service; Part 2: Harmonised EN
under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
ETS 300 384/A1: 1997 |
Date expired (31.12.2005) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 018-2 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
Compatibility and Radio Spectrum Matters (ERM); Transmitting equipment for
the Frequency Modulated (FM) radio broadcast service; Part 2: Harmonised EN
under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 302 018-2 V1.1.1 |
30.11.2007 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 054-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Meteorological Aids (Met
Aids); Radiosondes to be used in the 400,15 MHz to 406 MHz frequency range
with power levels ranging up to 200 mW; Part 2: Harmonised EN covering
essential requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 064-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Wireless Video Links (WVL)
operating in the 1,3 GHz to 50 GHz frequency band; Part 2: Harmonised EN
under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 066-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Short Range Devices (SRD);
Ground- and Wall-Probing Radar applications; Part 2: Harmonised EN under
Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 077-2 V.1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Transmitting equipment for
the Terrestrial - Digital Audio Broadcasting (T-DAB) service; Part 2:
Harmonised EN under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 186 V1.1.1 Satellite
Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Harmonised EN for satellite mobile Aircraft
Earth Stations (AESs) operating in the 11/12/14 GHz frequency bands covering
essential requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 195-2 V1.1.1 (3-2004) Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Radio equipment in the
frequency range 9 kHz to 315 kHz for Ultra Low Power Active Medical Implants
(ULP-AMI) and accessories; Part 2: Harmonised EN covering essential
requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 208-2 V.1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Radio Frequency
Identification Equipment operating in the band 865 MHz to 868 MHz with power
levels up to 2 W; Part 2: Harmonised EN under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE
Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 217-2-2 V1.1.3 Fixed Radio
Systems; Characteristics and requirements for point to point equipment and
antennas; Part 2 2: Harmonised EN covering essential requirements of Article
3(2) of R&TTE Directive for digital systems operating in frequency bands
where frequency co ordination is applied |
EN 301 751 V1.2.1 |
Date expired (31.5.2007) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 217-3 V1.1.3 Fixed Radio
Systems; Characteristics and requirements for point-to-point equipment and
antennas; Part 3: Harmonised EN covering essential requirements of Article
3(2) of R&TTE Directive for equipment operating in frequency bands where
no frequency co-ordination is applied |
EN 301 751 V1.2.1 |
Date expired (31.5.2007) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 217-4-2 V1.1.3 Fixed Radio
Systems; Characteristics and requirements for point to point equipment and
antennas; Part 4 2: Harmonised EN covering essential requirements of Article
3(2) of R&TTE Directive for antennas |
EN 301 751 V1.2.1 |
Date expired (31.5.2007) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 217-4-2 V1.2.1 Fixed Radio
Systems; Characteristics and requirements for point to point equipment and
antennas; Part 4 2: Harmonised EN covering essential requirements of Article
3(2) of R&TTE Directive for antennas |
EN 302 217-4-2 V1.1.3 |
31.3.2008 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 245-2 V.1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Transmitting equipment for
the Digital Radio Mondiale (DRM) broadcasting service; Part 2: Harmonised EN
under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 288-2 V.1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Short Range Devices; Road
Transport and Traffic Telematics (RTTT); Short range radar equipment
operating in the 24 GHz range; Part 2: Harmonised EN covering essential
requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 288-2 V1.2.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Short Range Devices; Road
Transport and Traffic Telematics (RTTT); Short range radar equipment
operating in the 24 GHz range; Part 2: Harmonised EN covering essential
requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
EN 302 288-2 V1.1.1 |
30.6.2008 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 291-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Short Range Devices (SRD);
Close Range Inductive Data Communication equipment operating at 13,56 MHz;
Part 2: Harmonised EN under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 296 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Transmitting equipment for
the digital television broadcast service, Terrestrial (DVB-T); Harmonised EN
under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 297 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum matters (ERM); Transmitting equipment for
analogue television broadcast service; Harmonised EN under Article 3(2) of
the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 326-2 V1.1.2 Fixed Radio
Systems; |
EN 301 753 V1.2.1 |
30.9.2008 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 326-2 V1.2.2 Fixed Radio
Systems; |
EN 302 326-2 V1.1.2 |
31.3.2009 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 326-3 V1.1.2 Fixed Radio
Systems; Multipoint equipment and antennas; Part 3: Harmonised EN covering
the essential requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive for
Multipoint Radio Antennas |
EN 301 753 V1.2.1 |
30.9.2008 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 326-3 V1.2.2 Fixed Radio
Systems; |
EN 302 326-3 V1.1.2 |
31.3.2009 |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 340 V1.1.1 Satellite
Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Harmonised EN for satellite Earth Stations
on board Vessels (ESVs) operating in the 11/12/14 GHz frequency bands
allocated to the Fixed Satellite Service (FSS) covering essential
requirements under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 372-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Short Range Devices (SRD);
Equipment for Detection and Movement; Tanks Level Probing Radar (TLPR)
operating in the frequency bands 5.8, 10, 25, 61 and 77 GHz; Part 2:
Harmonised EN under Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 426 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Harmonised EN for CDMA spread
spectrum repeaters operating in the 450 MHz cellular band (CDMA450) and the
410, 450 and 870 MHz PAMR bands (CDMA PAMR) covering essential requirements
of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 454-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Meteorological Aids (Met
Aids); Radiosondes to be used in the 1 668,4 MHz to 1 690 MHz frequency
range; Part 2: Harmonised EN covering essential requirements of Article 3(2)
of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 502 V1.1.1 Broadband
Radio Access Networks (BRAN); 5,8 GHz fixed broadband data transmitting
systems; Harmonised EN covering essential requirements of Article 3(2) of the
R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 302 510-2 V1.1.1 Electromagnetic
compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Radio equipment in the
frequency range 30 MHz to 37,5 MHz for Ultra Low Power Active Medical
Membrane Implants and Accessories; Part 2: Harmonised EN covering essential
requirements of Article 3(2) of the R&TTE Directive |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 303 035-1 V1.2.1 Harmonised EN
for TETRA equipment covering essential requirements under Article 3(2) of the
R&TTE directive; Part 1: Voice plus Data (V+D) |
EN 303 035-1 V1.1.1 |
Date expired (30.9.2003) |
Article 3(2) |
|
EN 303 035-2 V1.2.2 Harmonised EN
for TETRA equipment covering essential requirements under Article 3(2) of the
R&TTE directive; Part 2: Direct Mode Operation (DMO) |
EN 303 035-2 V1.2.1 |
Date expired (31.10.2004) |
Article 3(2) |
|
ETS 300 487/A1:1997 Satellite
earth stations and systems (SES); Receive-only mobile earth stations (ROMES)
operating in the 1,5 GHz band providing data communications; Radio frequency
(RF) specifications |
|
|
Article 3(2) |
Note 1:
Generally the date of cessation of presumption of conformity will be the date
of withdrawal ( “dow”), set by the European Standardisation Organisation, but
attention of users of these standards is drawn to the fact that in certain
exceptional cases this can be otherwise.
Note 2.1: The
new (or amended) standard has the same scope as the superseded standard. On the
date stated, the superseded standard ceases to give presumption of conformity
with the essential requirements of the directive.
Note 2.2: The
new standard has a broader scope than the superseded standard. On the date
stated the superseded standard ceases to give presumption of conformity with
the essential requirements of the directive.
Note 2.3: The
new standard has a narrower scope than the superseded standard. On the date
stated the (partially) superseded standard ceases to give presumption of
conformity with the essential requirements of the directive for those products
that fall within the scope of the new standard. Presumption of conformity with
the essential requirements of the directive for products that still fall within
the scope of the (partially) superseded standard, but that do not fall within the
scope of the new standard, is unaffected.
Note 3: In case
of amendments, the referenced standard is EN CCCCC:YYYY, its previous
amendments, if any, and the new, quoted amendment. The superseded standard
(column 3) therefore consists of EN CCCCC:YYYY and its previous amendments, if
any, but without the new quoted amendment. On the date stated, the superseded
standard ceases to give presumption of conformity with the essential
requirements of the directive.
Example : For
EN 60215:1989, the following applies :
|
EN 60215:1989
Safety
requirements for radio transmitting equipment (IEC
60215:1987) [The
referenced standard is EN 60215:1989] |
[There is no
superseded standard] |
- |
Article
3.1.a (& Article 2 73/23/EEC) |
|
Amendment
A1:1992 to EN 60215:1989 (IEC
60215:1987/A1:1990) [The
referenced standard is EN 60215:1989 |
Note 3 [The
superseded standard is EN 60215:1989] |
Date expired (01.06.1993) |
|
|
Amendment
A2:1994 to EN 60215:1989 (IEC
60215:1987/A2:1993) [The referenced
standard is EN 60215:1989 |
Note 3 [The
superseded standard is EN 60215:1989 + A1:1992 to
EN 60215:1989] |
Date expired (15.07.1995) |
|
Note 4: EN 301 489-1 contains the common EMC emission and
immunity requirements for all radio equipment and must be used together with
the appropriate radio part of this standard, to demonstrate presumption of
conformity to article 3.1.b of the directive.
Note:
In addition standards published under Directives 2006/95/EC, 2004/108/EC,
90/385/EEC and 93/42/EEC may be used to demonstrate compliance with articles
3.1.a and 3.1.b of Directive 1999/5/EC.
Products are presumed to comply with the Directive when they meet the
requirements within the usage conditions for which they are intended.
The list published in OJ C 225 of 2006-09-25 replaces all the previous
lists published in the Official Journal of the European Union.
© 2005, 2010 Professional Testing & Consulting Ltd. All rights reserved.
